Field Trials Confirm: Aspen Trees May be Modified for Easier Access for Biorefinery Production
Field trials of transgenic aspen trees have confirmed that genetic modification is indeed a possible avenue for rendering wood less resistant to breakdown into components suitable for making biofuel, “green” chemicals or bio-based materials.
Research just out shows not only how to modify tree plants for superior yield of desired sugar-based content, but also offers industry or investors proof-of-concept results from pilot-scale trials performed for the most successful combinations or “constructs” in science speak.
Most innovations require Proof of Concept to survive past the early stages of product development. It is a formalised way of providing evidence that demonstrates that a design concept or business proposal is feasible.
For the last decade, Bio4Energy has shepherded field trials of hardwood species such as aspen, under the leadership of professor Ewa Mellerowicz, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
Collaboration partners include programme manager Leif Jönsson’s research team at Umeå University, as well as Bio4Energy research leaders at RISE Research Institutes of Sweden, the Wallenberg Wood Science Centre and others.
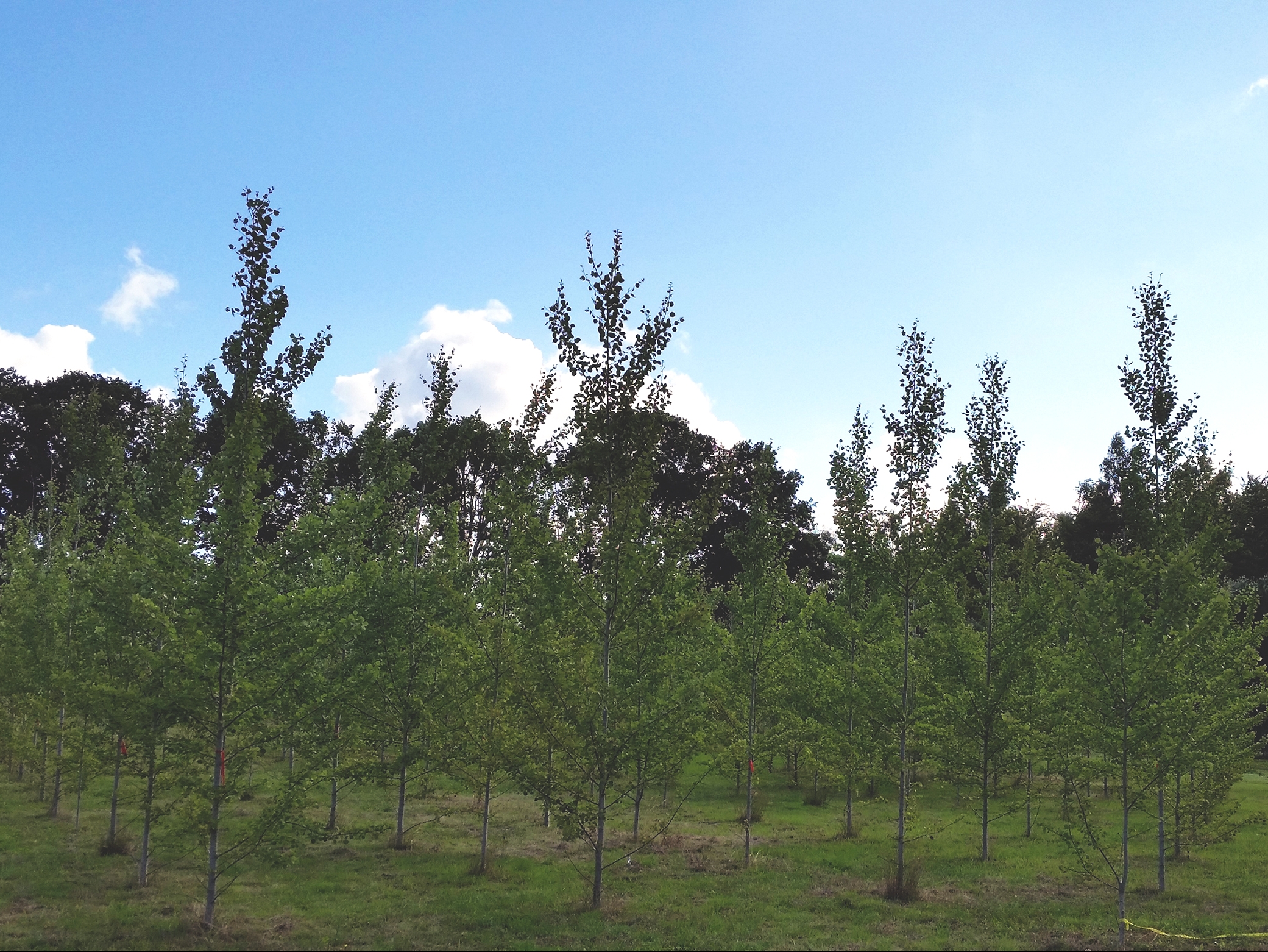
The results are expected to bring considerable benefit to the scientific community, given that no less than 32 so-called lines of genetically modified aspen trees previously evaluated only in greenhouse trials, have been grown and studied for five years in field plantations in Sweden.
“Whereas there are many examples of genetically modified trees that are improved in the greenhouse experiments, the trees with improved properties in the field are exceptional”, Mellerowicz told Bio4Energy Communications.
The fact that the field trials used material pre-selected from extensive greenhouse experiments, testing very large numbers of constructs, let the scientists bring about optimal results in the field. This way, the trees grew faster (produced more wood) and were more ready to release sugar-rich polymers, which are desired input materials for making biorefinery products.
“By [implementing a] systematic long-term and multi-level testing strategy, we were able to identify certain unknown function genes that improve field productivity and saccharification yield”, according to Mellerowicz.
Moreover the best transgenic lines were processed in a pilot-scale reactor, mimicking industrial conditions, to provide proof of concept for the strategy.
“The identified genes will be of particular interest to modify, using non-transgenic approaches to produce feedstocks that are GMO free, but have improved performance in the field and in the biorefinery”, she said.
This means that more research is needed before the findings can be demonstrated as a new technology, but the advantage created is that genes have been identified that could be targets for it.
Contact
Ewa Mellerowicz, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences — Bio4Energy Forest-based Feedstocks, affiliation with the Umeå Plant Science Centre
Scientific article
The article Field testing of transgenic aspen from large greenhouse screening identifies unexpected winners, is published in the Plant Biotechnology Journal January 2023.
The authors are acknowledged as follows: Donev EN, Derba-Maceluch M, Yassin Z, Gandla ML, Sivan P, Heinonen SE, Kumar V, Scheepers G, Vilaplana F, Johansson U, Hertzberg M, Sundberg B, Winestrand S, Hörnberg A, Alriksson B, Jönsson LJ and Mellerowicz EJ.
 Bio4Energy
Bio4Energy