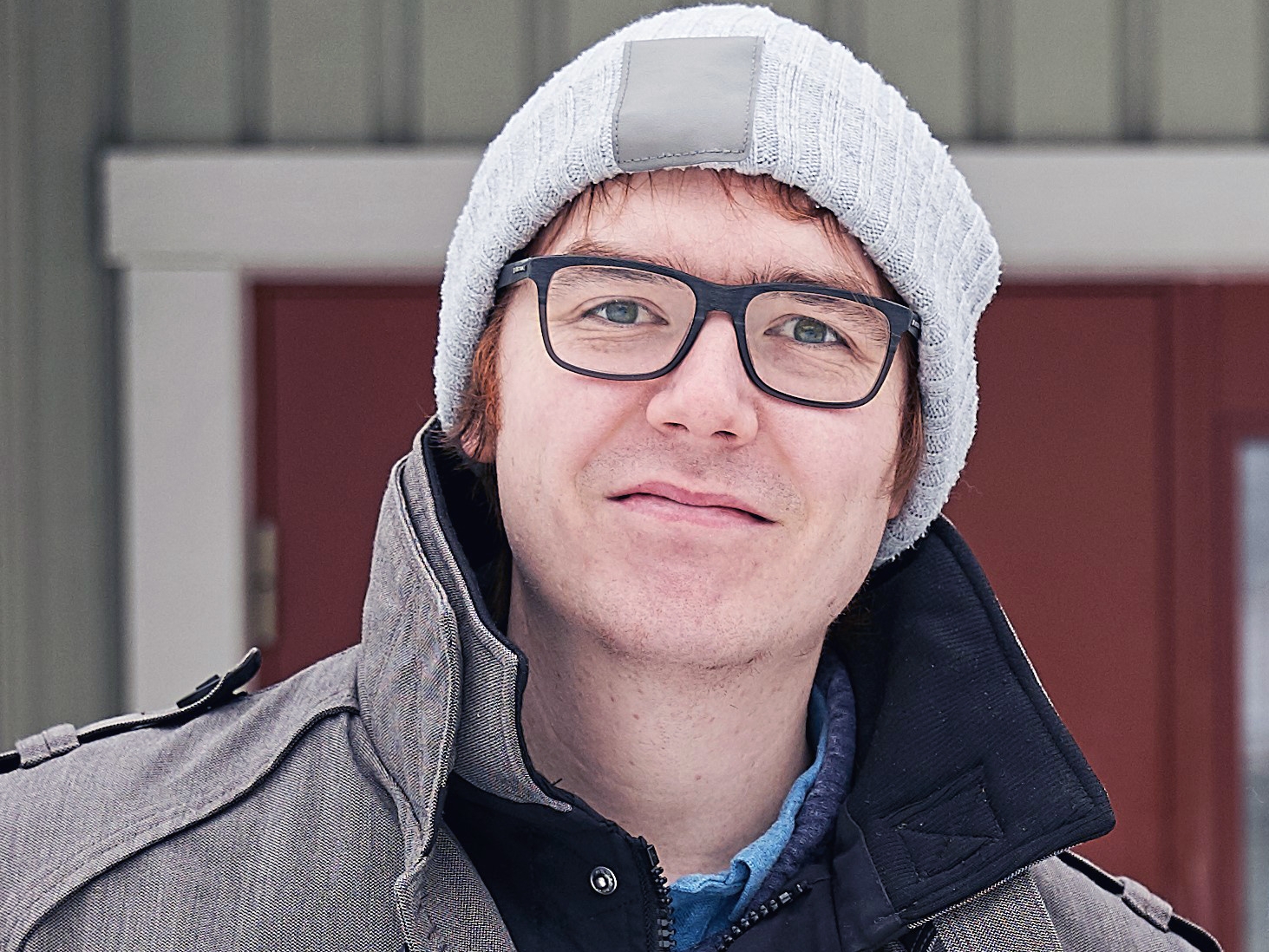
A Bio4Energy PhD student at Umeå University (UmU) has won a prize for his work on waste management, bio-based materials and recycling, by a Sweden-based institute that represents his home country, France.
In his research, Pierre Oesterle investigates ways to re-use by products from forestry industry; and the ways in which these can made to remove micropollutants from wastewater.
In doing so, Oesterle is one of the forbearers in the field of bio-based chemicals and materials, who aim to tackle the rapidly expanding problem of micropollutants that leak into the environment as a result of pharmaceutical drug use.
For the most part, this kind of pollution is not being picked up and filtered out by current wastewater treatment plants.
Using sorbents for treating wastewater is not new in itself, but the ones on the market are based on activated charcoal. In a context of aiming to contain climate change, such materials are not deemed environmentally friendly.
A sorbent–whether based on petrochemicals or biomass–is a material that acts as a molecular sieve, which attracts micropollutants and holds them to it, in a layer of thin film.
“My research tries to design bio-based activated biochars from waste of mining and forestry industry to replace those activated carbons in wastewater treatment plants”, Oesterle writes in an e-mail to Bio4Energy Communications and; “to regenerate or recycle these spent sorbents using hydrothermal deconstruction.
“The idea behind this technology is to use a low temperature, but a high pressure; to degrade the contaminants adsorbed on the surface of the activated biochar and to check the regeneration efficiencies of the material afterwards”.
Circular economy
The French Institutes of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Norway and Sweden in their Nordic Award 2023 are targeting “outstanding achievements” to pave the way for a circular economy, by young French nationals.
“This award aims to promote cultural and scientific cooperation between France and the Nordic countries and to reward the outstanding achievements of young researchers”, according to the call for applications.
Oesterle will receive his prize from the hand of the French Ambassador to Sweden, 20 June. It comes with a paid-for trip to meet likeminded colleagues in the French region of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, so that more cross-border and circularity friendly research may be spawned.
This edition of the FINA prize aims to help achieve three of the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Sustainable consumption and production, climate change abatement and zero hunger.
“Few removal [or] degradation processes are currently used, such as ozonation or activated carbon. The drawback of using activated carbon is the unsustainability of the technique; as when the adsorbent is spent, most of the activated carbons end up incinerated or in landfill; inducing potential secondary pollution. Moreover, most activated carbons are based on non-renewable resources (coal), which do not meet the SDGs”, Oesterle wrote.
Event: Webinar via Zoom, in which the FINA finalists present their research, hosted by the French Institute of Sweden. Thursday June 8, from 1:30 p.m. All welcome to attend.
Research platform: Bio4Energy Environment and Nutrient Recycling
About Pierre Oesterle: Personal page and list of publications, Umeå University
Circular economy is a system of production, exchange and sharing that allows for social progress, preservation of natural capital and economic development, as defined by the Brundtland Commission of the United Nations.
 ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom