Training on Wood Biology, Biotechnology Fills Gap for Advanced Students of Biorefinery
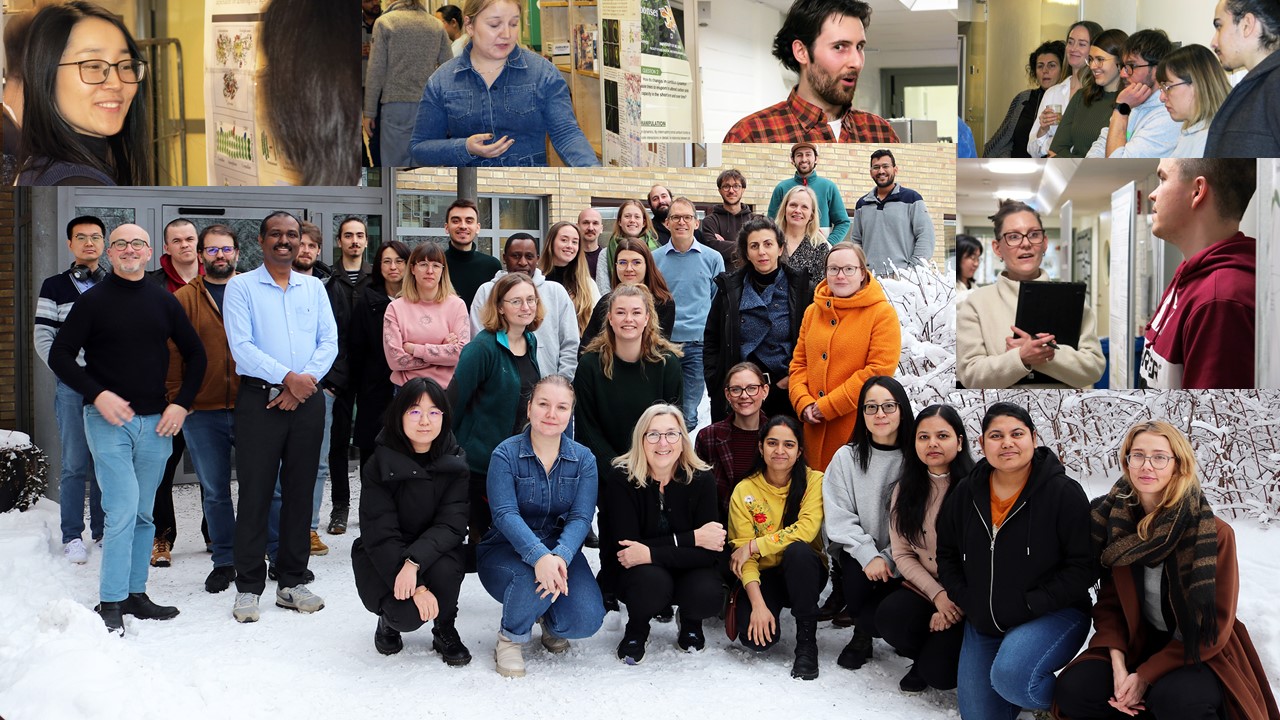
Mini FEATURE. Northern Sweden, last week was home to advanced students affiliated with universities in Finland, Czech Republic, Belgium and Sweden—spending an intensive week at the city of Umeå—to learn about the frontline of science of wood biology and biotechnology.
Hosted by a leading wood biologists, Ewa Mellerowicz of the Umeå Plant Science Centre and Bio4Energy, this ad-hoc training is offered for the second time to equip advanced students interested in wood biology, tree breeding and biorefinery development with an edge.
“This course fills a gap and provides an overview of biological processes, explaining how they lead to developing different kinds of wood, and how they affect wood traits of economic importance”, the online course description says:
“Lectures and seminars are given by world experts in the field”.
“This course fills a gap and provides an overview of biological processes, explaining how they lead to developing different kinds of wood, and how they affect wood traits of economic importance. Lectures and seminars are given by world experts in the field”.
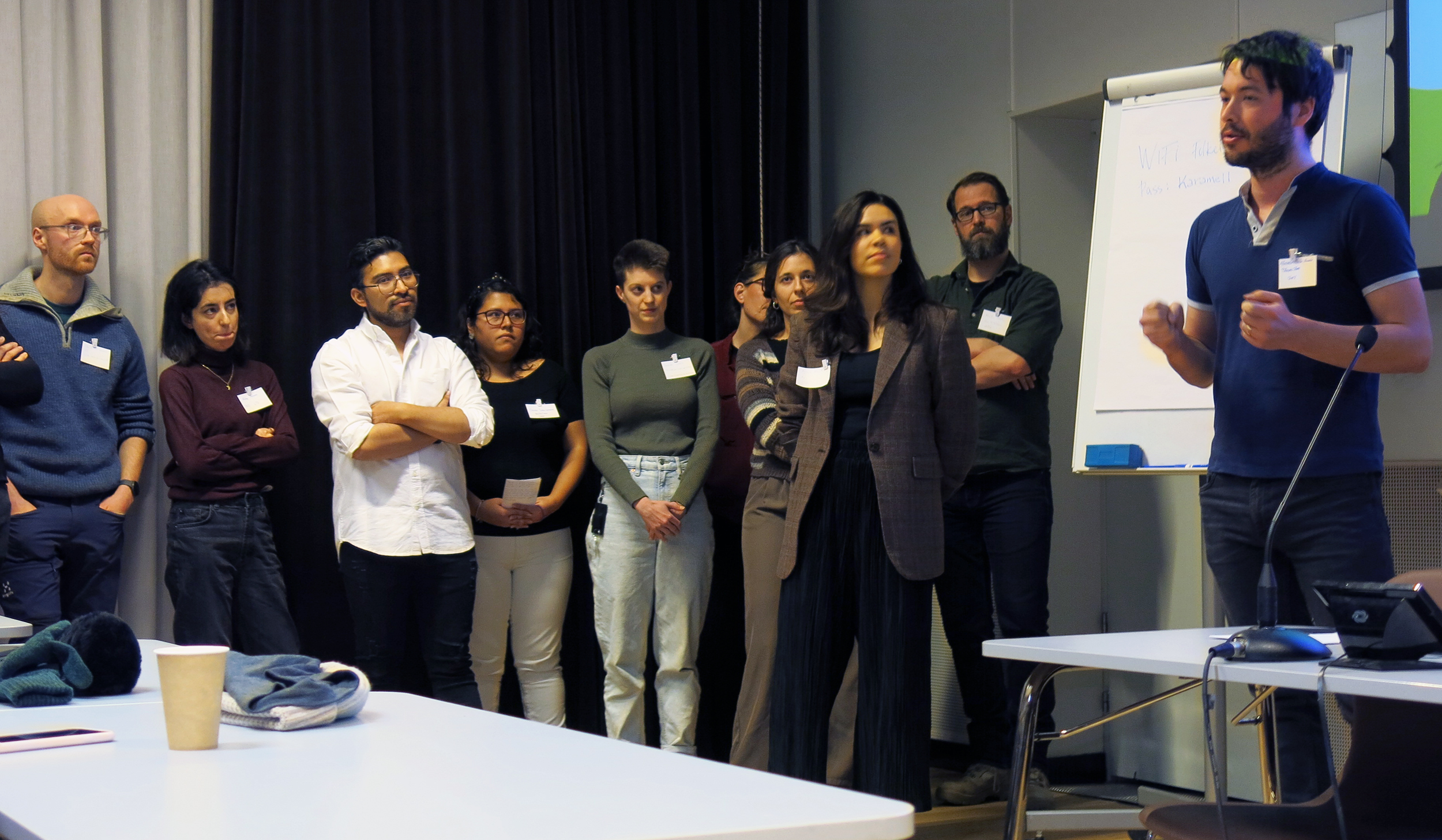
When I stop by, the students are in full swing presenting posters to each other, a common feature both in advanced education and at scientific conferences.
“It is going great”, Hannele Tuominen, professor at the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU) and platform leader in Bio4Energy, greets me.
“We have 20 students and here they learn to attack the issues we are discussing from every angle. We have a lineup of experts here to teach them [on location]. This is our strength”, Tuominen says.
“Most students have a molecular biology or wood chemistry background”, Mellerowicz fills in. She also has an affiliation with the Umeå branch of SLU. She agrees with a smile that it is great but exhausting;
“The students are here all week with a full programme in the daytime and then social activities in the evening”.
Most of them are much too busy liaising with each other to talk to me, but Bio4Energy student Anna Renström of Umeå University, is here just for the evening poster session.
“We have a new publication on wood formation in hybrid aspen that lets us know more about the lignin formation. Now we need to apply [the concept] to other species such as spruce and we need to conduct field trials to understand whether it really works”, she says expertly.
Renström is being supervised by Tuominen and others who are part of the teaching line up and I think to myself that it shows.
Contact
Ewa Mellerowicz, Umeå Plant Science Centre — Affiliation with the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
For more information
Wood Biology and Biotechnology, 5 ECTS
 ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom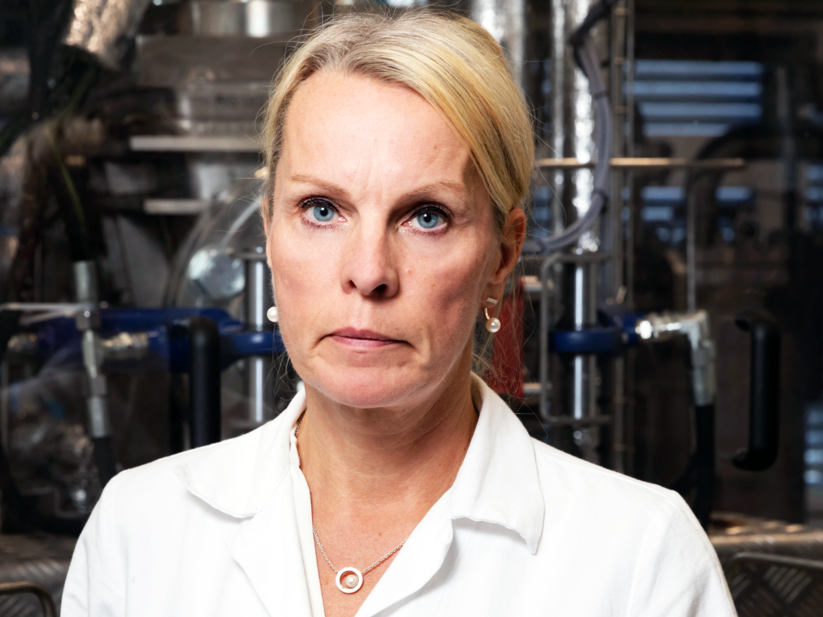 Bio4Energy
Bio4Energy
 AnnaStrom
AnnaStrom










 ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom
 ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom