Creation of Value Chains for Biochar as Alternative to Fossil Fuels in Industry in New Project
A grouping of Bio4Energy experts on systems analysis have won a large grant to map out new value chains for the production of biochar, a type of charcoal, for use in industry or as a carbon sink.
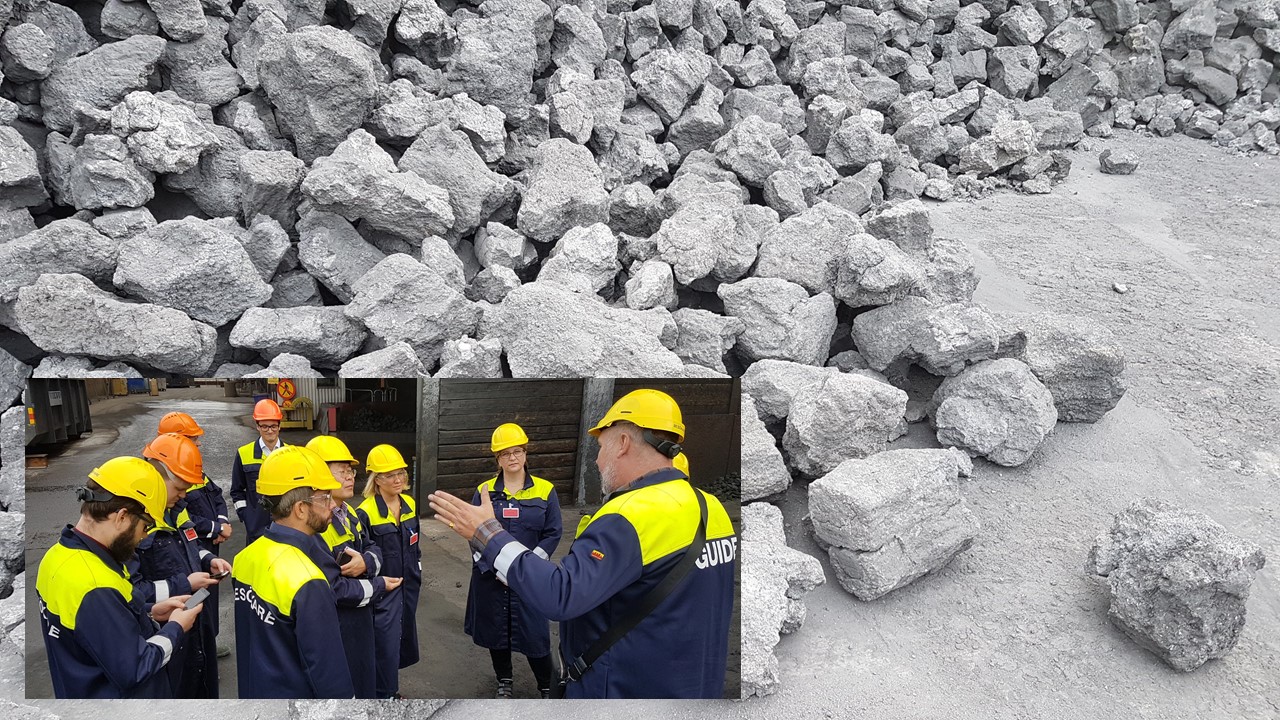
Biocarbon – with the application biochar, which is a form of biomass pre-treated in high temperatures and in a limited-oxygen environment – is being extensively investigated as an alternative to fossil coal in industrial processes, such as in the iron and steel industry.
However, with each major new replacement product comes the need to ascertain that it is sustainable in terms of economics, as well as social and environmental impacts; and that it can form or fit into the context it is in.
In the new project, PhD students will work together to map out a comprehensive scheme for value chains from raw material supply to industrial markets for this renewable technology.
In the new project, three new PhD students will work together to map out a comprehensive scheme for value chains from raw material supply to industrial markets for this renewable technology. They will perform their work from the Bio4Energy partner universities Luleå University of Technology and the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU), both located in northern Sweden.
The project is part of a national Graduate School in Energy Systems, funded by the Swedish Energy Agency and coordinated by Linköping University (LiU), Sweden.
In addition to new value chains for production, the project will deliver policy recommendations and create a pool of in depth knowledge about markets, tools for policy-making and technology.
In addition to new value chains for production, the project will deliver policy recommendations and create a pool of in depth knowledge about markets, tools for policy-making and technology.
“We are going to develop knowledge about raw material sources for biocarbon and inventory flows of biomass in Sweden”, said David Agar, senior lecturer at SLU.
“We will look at surplus sources in pulp and paper and saw dust, forestry residues…. It doesn’t mean that we have to stick only with the big industries. We could look at recycled products or waste”, Agar said.
When it came to the potential of biocarbon and biochar as an alternative technology to fossil fuels, Agar said that the project would map both potentials and limitations.
“You cannot expect to have exactly the same process. You have to have something to compensate for the high carbon content of fossil fuels. You have to have a very pure carbon source, with good heating properties”, he added.
Carbon source still needed despite electrification
While it is true that there is a sweeping electrification underway, there are still industrial processes that require either a fossil or alternative source of fuel or gas.
”In fossil fuel-free steel production the plan is to use electricity both in the process of direct reduction and in the electric arc furnace”, according to project leader Elisabeth Wetterlund, Luleå University of Technology (LTU).
Direct reduction is the removal of oxygen from iron ore or other iron bearing materials in the solid state, while an electric arc furnace is a type of furnace used in steelmaking to melt and refine steel scrap or other raw materials, transforming them into molten steel.
Professor Wetterlund explained that while both of these processes are powered by renewable electricity, the addition of a fossil or renewable carbon source is still required to complement the hydrogen that is used for the reduction.
“Despite the electrification we still need carbon to produce the kind of steel we want and create appropriate conditions inside the electric arc furnace. This is where biochar comes in, as a replacement for coal and coke-oven coke”, she wrote in reply to questions.
Contacts
Elisabeth Wetterlund – Bio4Energy Systems Analysis and Bioeconomy, Affiliation with LTU
David Agar – Bio4Energy Systems Analysis and Bioeconomy, Affiliation with SLU
Dan Bergström – Bio4Energy Systems Analysis and Bioeconomy, Affiliation with SLU
Robert Lundmark – Bio4Energy Systems Analysis and Bioeconomy, Affiliation with LTU
Related projects
Paving the road for introducing renewable energy carriers in large industries – Bio4Energy
Related news
Three-year Project Could Set Steelmaker Well on Way to Hydrogen-based Operations – Bio4Energy
Phase Out of Fossil Coal in Sweden’s Iron, Steel Industries on Cards – Bio4Energy
Role of Forests in Reining in Climate Change, Producing Energy – Bio4Energy


 Bio4Energy: No copying or sharing
Bio4Energy: No copying or sharing ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom Bio4Energy
Bio4Energy
 ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom Dreamstime
Dreamstime ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom AnnaStrom
AnnaStrom











 BioFuel Region
BioFuel Region