A consortium of Bio4Energy researchers has scored a grant for developing bio-based plastic to deliver prototypes of consumer products by project end, three years from now.
It involves a number of industrial and business partners who will provide either facilities and input material for experimental trials or develop consumer products, such as lampshade prototypes and a foam to go into packaging materials, respectively. The resulting products will be tested for their biodegradability.
It involves a number of industrial and business partners who will provide either facilities and input material for experimental trials or develop consumer products, such as lampshade prototypes and a foam to go into packaging materials, respectively. The resulting products will be tested for their biodegradability.
Global plastics production has exploded since the early 20th century and virtually all of it derives from fossil-based petrochemicals. In 2018, it stood at 359 million metric tons per annum.
At the end of life, over three fourths of plastics go into landfill. The breakdown of plastic made from petrochemicals generally takes hundreds of years and comes with leakage into the environment, especially for the kinds that degrade to microplastics during the composting process.
Plastic pollution has become an urgent global problem.
Innovation-to-consumer product value chain
In northern Sweden, Bio4Energy experts on the development and use of algae biomass for products and applications are proposing to tackle the issue head on by linking up actors in a research innovation-to-consumer product value chain.
The Swedish Energy Agency—which is not only a government agency, but also a research funder—has agreed to part sponsor the development of more affordable polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), which is a type of bio polyester that has the moldability of traditional plastics.
So far, PHA as a plastic alternative has had limited uptake, mainly because of the high cost of the feed for bacteria that make it. Here is where the Bio4Energy research comes in.
The scientists will identify strains of microalgae which, using sunlight and carbon dioxide, make biomass that the bacteria like to eat. The algae themselves will feed off industrial flue gases and wastewater produced at premises of regional energy utility Umeå Energi, which the green algae help clean during the while.
The scientists will identify strains of microalgae which, using sunlight and carbon dioxide (CO2), make biomass that the bacteria like to eat. The algae themselves will feed off industrial flue gases and wastewater produced at premises of regional energy utility Umeå Energi, which the green algae help clean during the while. The project also involves a utility that delivers drinking water, as well as handles sewage water treatment and waste recycling in the greater Umeå area; Vakin.
Algae research expert Christiane Funk will lead the project from Umeå University (UMU) and collaborate with Francesco Gentili, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU), whose team operates development facilities at the Umeå Energi Dåva site. His colleague Carmen Cristescu will perform a life cycle assessment of the process. Bio4Energy programme manager Leif Jönsson’s group at UMU is also part of the project.
“We are going to use algae as feed for bacteria producing PHA, a type of bio polyester. The bacterial cultivation will be scaled up to litres by RISE Processum”, professor Funk said.
Membership company Processum at RISE Research Institutes of Sweden is one Bio4Energy’s strategic partners. Bio4Energy alumnus Pooja Dixit will lead this part of the work.
High cost of PHA limits market uptake
PHA as an alternative to petrochemical polymers for plastic production has had limited market uptake because of its high cost.
“It would be perfect to use PHA instead of plastic. We try to make it cheaper so that PHA can compete with fossil-based plastic and we also try to make the process more sustainable by using microalgae. We have to test which bacteria like which type of sugars [or carbohydrates] to produce PHA”, professor Funk said.
“It would be perfect to use PHA instead of plastic. We try to make it cheaper so that PHA can compete with fossil-based plastic and we also try to make the process more sustainable by using microalgae. We have to test which bacteria like which type of sugars to produce PHA”.
Downstream, two companies stand ready to turn the PHA into products.
In Stockholm, Interested Times Gang will take PHA from the project, to attempt 3D printing lampshades.
SME Cass Materials at Örnsköldsvik aim to mix the PHA with starch to improve an existing form of packing material in terms of its environmental footprint. The company describes the material as a “next generation bio-based foam that is lightweight with good mechanical strength and insulation properties for the packaging industry”.
Finally, Biocompost of Skellefteå is going to test the materials produced, particularly the ones that have a starch component, to see how long they take to biodegrade.
“We are going to work on the microalgae and the bacteria… and feed the carbohydrate to the bacteria in a two-step process”, Funk explained;
“We are going to test different algal strains [to ascertain] which produce the best feed for the bacteria”.
Globally, nine per cent of plastic waste is recycled and 12 per cent is incinerated. In countries that have ocean shorelines, each year between 4.8 million and 12.7 million metric tons of plastic waste are discarded into the sea. Source: Encylopaedia Britannica.
Project title: Waste2Plastic – Circular economy, recycling of CO2, nitrogen, phosphorus and water for bioplastics in a sustainable society
Funders: Swedish Energy Agency’s strategic innovation program RE:Source, which focuses on developing circular and resource-efficient material flows that are within planetary “boundaries”. The joint contribution of industrial partners is expected to match the SEA grant.
Bio4Energy research leaders involved
Christiane Funk, project manager and Leif Jönsson – Bio4Energy Biopolymers and Biochemical Conversion, affiliation with Umeå University
Francesco Gentili – Bio4Energy Environment and Nutrient Recycling, affiliation with the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
Carmen Cristescu – Bio4Energy Systems Analysis and Bioeconomy, affiliation with the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
Lalie Kossatz and Pooja Dixit – Processum at RISE
Business partners: Umeå Energi, Vakin, Cass Materials, ITG Studio, Biocompost
Related projects
Circular and sustainable production of bioplastics with the help of photosynthetic microorganisms – Proof of concept – Bio4Energy
Waste2Plastic – Production of bioplastic from algal biomass generated from wastewater – Bio4Energy
Related news
Microalgae that Thrive in Cold Climate Clean Wastewater, Give Biomass for Renewable Plastics – Bio4Energy
Sweden’s Bioeconomy Arena to Open by Early 2025: Bio4Energy Researchers Stopped by – Bio4Energy
Breakthrough Innovation: Hydrogels from Norwegian Kelp to Be Commercialised – Bio4Energy








 ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom

 RISE
RISE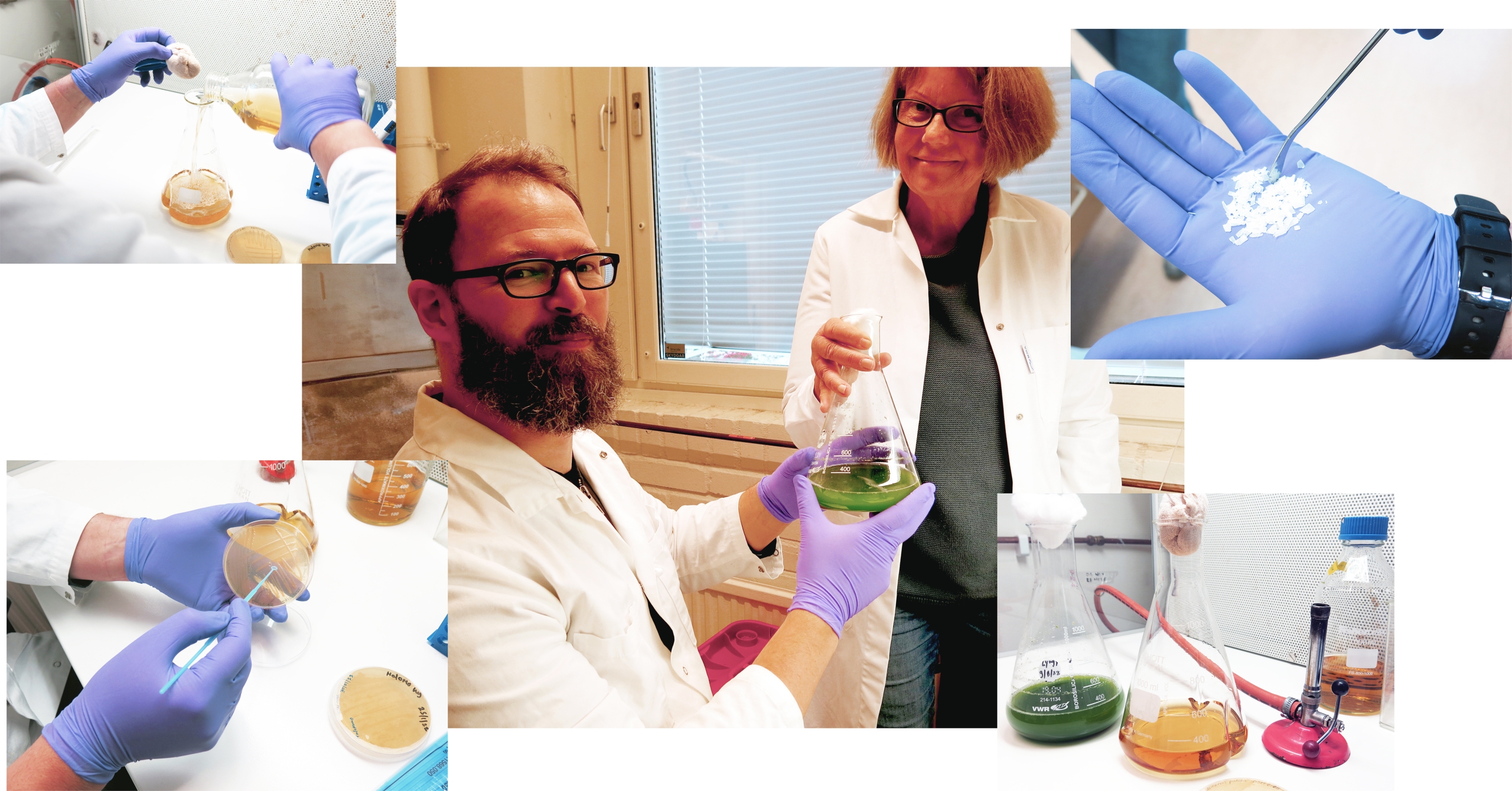 ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom
 ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom Bio4Energy
Bio4Energy ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom