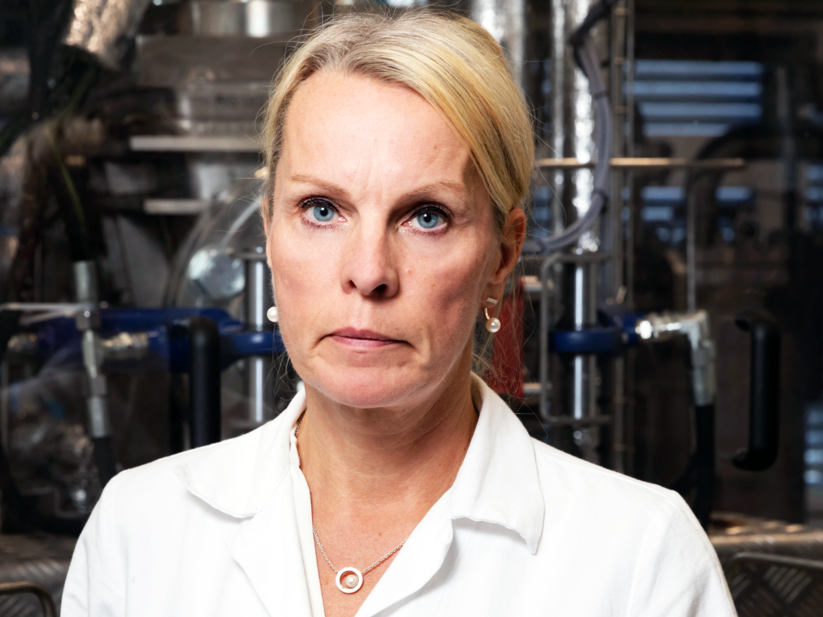
Seeing Possibilities: Meet Bio4Energy’s Coordinator for Swedish funder BioInnovation
Bio4Energy’s new coordinator for BioInnovation, Swedish funder of bio-based innovations, is Ulrika Rova, professor at Luleå University of Technology.
Rova sees herself not only as the research environment’s representative with an overview of possibilities for applying for funds, but also as a facilitator and a bearer of information to potential collaboration partners representing other organisations in the bio-based sector.
“I need first to study the offer and future calls for projects, but then I can be a channel for information going both ways”, Rova told Bio4Energy Communications.
Structured as a member organisation, BioInnovation evaluates and funds a range of projects on behalf of the Swedish national funding agencies Vinnova, Formas and the Swedish Energy Agency. Bio4Energy is a founding member, or a “party”, and involved in its divisions on Materials, as well as Chemicals and Energy.
Structured as a member organisation, BioInnovation evaluates and funds a range of projects on behalf of the Swedish national funding agencies Vinnova, Formas and the Swedish Energy Agency. Bio4Energy is a founding member, or a “party”, and involved in its divisions on Materials, as well as Chemicals and Energy.
“Our vision is that Sweden will have transitioned to a circular economy by 2050. We are going to create optimal conditions for developing the Swedish bio-based sector and create sustainable solutions for a global market”, the Swedish version of BioInnovation’s website said (ed’s translation).
Two projects headed up by Bio4Energy research leaders stand out: Joint production of edible mushroom and advanced biofuel, as well as production of food-grade prebiotics from forest resources and sea squirts, a colonial tunicate.
The latter is a small sea-living invertebrate that has an outer protective cover; a tunic consisting of a cellulose-like substance; which is the target for developing prebiotics for human and animal consumption.
Rova led the prebiotics project. Given that Bio4Energy is a member since 2015, I want to know what might promote a more high-profile participation in BioInnovation-funded projects.
“The requirement of 50 per cent co-funding by proprietary users, that is an industrial partner, could be perceived as a challenge. As an [academic] researcher, you need to have a good contact network in industry”, Rova said.
“I will be participating the annual and biannual meetings and provide an overview of possibilities going both ways”, she said.
Professor Ulrika Rova is a veteran member of Bio4Energy. She served as deputy director of the research environment during its second five-year mandate, ending in 2019. Instrumental in developing education and training, she was the first head of the Bio4Energy Graduate School. She is a senior member of one of Bio4Energy’s research platforms, Biopolymers and Biochemical Conversion. Her home organisation is Luleå University of Technology where she is part of a Paul Christakopoulos' research group specialising in biochemical process technology. In later years, the group has been focusing on carbon dioxide capture and reuse, as well as bioprocesses for upcycling of plastics and managing EU projects.
Contact
Ulrika Rova, Bio4Energy Coordinator for BioInnovation — Affiliation with Luleå University of Technology
For more information
Bio4Energy Biopolymers and Biochemical Conversion Technologies
Related News (In Swedish)
Det stora blå – med enorm potential i framtidens hållbara utveckling – BioInnovation
Inhemsk odling av delikata matsvampar i sikte – och biodrivmedel på köpet – BioInnovation
Svensk innovation kan ge billigare matsvampar – BioInnovation
Fördelen med att odla läckra svampar på björkved – BioInnovation
 Bio4Energy
Bio4Energy
 Dreamstime
Dreamstime ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom Svebio
Svebio BioFuel Region
BioFuel Region ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom ©AnnaStrom
©AnnaStrom
 LTU
LTU